python
Introduction to version control
Programs are built in an iterative manner, piece by piece. Often software applications are developed in teams and all team members must have access to the same program code. New versions of the program code are developed throughout the phases of the development project and sometimes there is a need to downgrade to an earlier version of the program. It’s also important to make sure that program code that has previously been written won’t disappear or get deleted by accident.
These are the reasons for using version control.
Git and GitHub
A distributed version control tool called Git is used on this course (and often in professional software development as well) to manage version control. Distributed version control means that there is a shared storage (a repository) for program code which is used to create local copies of the program code on the user’s own computers. Up-to-date information is fetched from the shared, remote repository (referred to as ‘pull’) and new local changes are loaded into the remote repository (referred to as ‘push’).
GitHub is a freely available website where you can store the source code of your Git projects. It is also the largest open code repository and practically all professional programmers use GitHub in one way or the other.
To use GitHub, you must register a user account at https://github.com/.
Once you have signed up, you can create your own remote repositories for your projects on GitHub.
There are two ways you can create a repository for your own Python programs: either directly on GitHub or by using PyCharm. Let’s look at the first method.
Creating a repository on GitHub
Let’s start by creating your own GitHub repository for a project:
- Sign up to GitHub at https://github.com/.
- Once you are logged in, click the New button next to Repositories.
- Create yourself a private repository by using the settings in the image below.
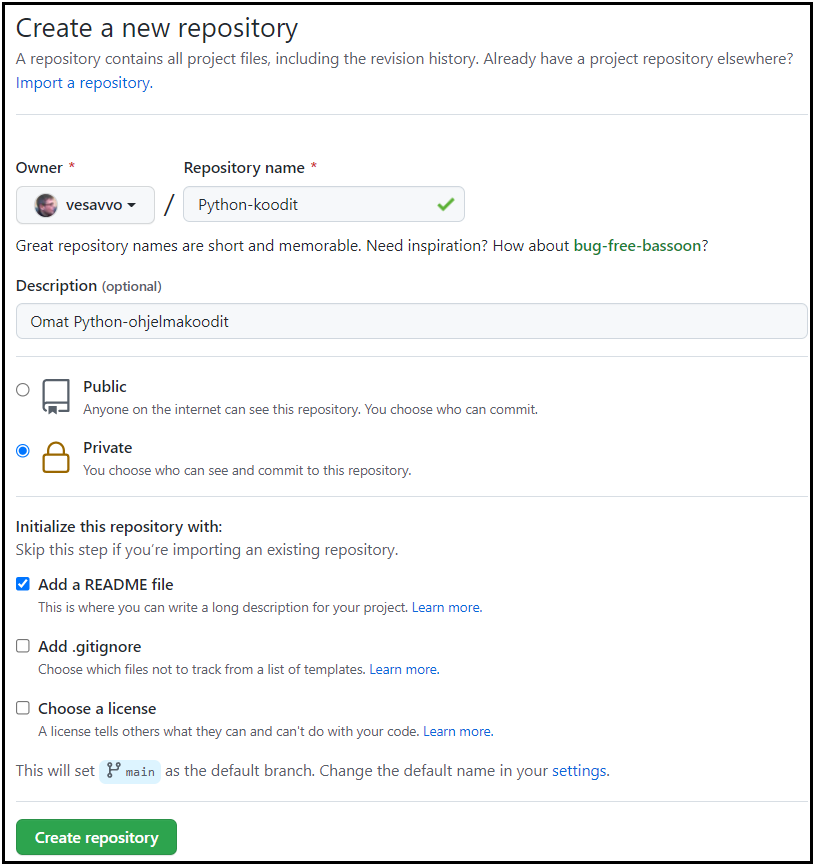
Next you will give PyCharm access to your repository.
-
Select the GitHub account you are using. Press Ctrl/Alt S. Select Version Control / GitHub /Add and enter your GitHub credentials.
-
Connect the repository to your Python project. In PyCharm, select VCS / Get from Version Control and select Clone to retrieve the Git repository you created on GitHub. PyCharm will create a new project that uses the GitHub repository.
If the GitHub repository does not yet exist, you can skip the second step and select VCS / Create Git Repository instead. In this case the repository will be created based on the PyCharm project and you can choose which files to store.
Once you have connected your project to a GitHub repository, a new Git tab will appear on PyCharm menu bar.
Using the repository
Now we will look at how GitHub can be used if there is just one developer. With a single developer there is no concern of files to be modified by several developers simultaneously. We will also assume that there will not be a need to separate the development project into several branches. You will learn more advanced use of Git as a co-operative platform at the beginning of the course project.
- Use the Git / Pull command every time you start working. The command will fetch all possible updates from the remote repository on GitHub.
- Every time you have finished some work, commit your changes using Git / Commit. The changes will create a new checkpoint that you can return to if needed. At minimum, commit your changes every time you are planning to stop working.
- When you stop working, use the Git / Push command. The command will copy all your locally committed changes to the remote repository on GitHub.
You can explore the development branch and checkpoints on GitHub.
Every time you create a new file, PyCharm will ask if you want the file to be included in version control. All source code, images and other valuable files should be stored on GitHub. On the other hand, configuration files and IDE-related data should be left out from version control. Also, any files containing passwords should not be saved to version control due to security reasons.